- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-10-24 Origin: Site







CNC routers have revolutionized industries by automating cutting, engraving, and shaping materials with precision. These machines have made it possible to create intricate designs with unmatched efficiency.
In this article, we will explore the various applications of CNC routers and how they impact industries like woodworking, prototyping, and sign-making. You'll learn how these versatile machines enhance productivity and accuracy across multiple fields.
CNC routers have transformed woodworking and furniture production by offering precision and speed. These machines make it easier to craft high-quality wood products at scale while maintaining detailed accuracy.
Cabinet Making: One of the most common applications of CNC routers is in the creation of custom cabinetry. By automating the cutting, drilling, and carving processes, CNC routers help manufacturers produce complex designs with consistent quality, reducing the time spent on manual labor. From intricate door panels to elegant moldings, CNC routers ensure that every piece matches the design specifications perfectly.
Furniture Production: CNC routers play a key role in the furniture industry by allowing designers to craft intricate components for furniture, such as chair backs, armrests, and drawer fronts. The machine's ability to handle complex shapes and achieve consistent results significantly speeds up production, making mass production of custom furniture more feasible.
Wood Carving: Beyond functional components, CNC routers are used by artisans and manufacturers to produce decorative wood carvings. From fine detailing in sculptures to highly intricate patterns in cabinetry, CNC routers provide the precision required to execute designs that would be time-consuming and difficult to achieve by hand.
Tip: For businesses in woodworking, investing in a CNC router can increase output and reduce the time it takes to deliver custom products, allowing for higher profit margins.
CNC routers are particularly valuable in the world of product development and prototyping, where speed and precision are crucial. The ability to quickly produce accurate prototypes enables designers to test and iterate on new ideas before moving into mass production.
Rapid Prototyping: Traditionally, prototypes required time-consuming manual carving or costly outsourcing to specialized shops. CNC routers have transformed this process by automating it. Designers can create multiple iterations of a prototype quickly, with each version being just as precise as the last. This significantly accelerates the design phase and allows companies to test different variations without incurring additional costs.
Engineering and Architecture: CNC routers are frequently used by engineers and architects to create precise models and components for buildings, machinery, and other projects. These machines are ideal for producing 3D architectural models that accurately reflect the finished product, allowing stakeholders to assess the design before actual construction begins. For example, CNC routers are used to cut models of urban landscapes or parts for mechanical systems with extreme precision.
Customization: With CNC routers, modifications to designs can be made at a moment's notice. This allows companies to easily adapt prototypes based on feedback or test results, providing flexibility and facilitating faster product development cycles.
One of the most widespread uses of CNC routers is in the sign-making and advertising industry. CNC routers can produce high-quality, customized signage in a variety of materials, including wood, acrylic, plastic, and metals. Their precision is particularly useful when creating detailed logos, lettering, and other promotional designs.
Custom Signs: CNC routers are often employed to create unique signage for businesses, schools, and organizations. They offer the flexibility to work with different materials, including woods for rustic signage or plastics for modern and sleek designs. The precision of the CNC router ensures that every letter, graphic, or symbol is perfectly aligned and clear, creating professional-grade signage that attracts attention.
Logo and Branding: Logos and branding materials are often created using CNC routers, which can engrave or cut designs into a variety of surfaces. This process offers a higher level of accuracy than hand-carved methods, allowing businesses to achieve a high level of consistency across their branding efforts.
Advertising and Displays: Beyond signage, CNC routers are used to create promotional displays and retail fixtures. From customized shelving units to intricate display stands, CNC routers make it possible to create one-of-a-kind pieces that match specific advertising and marketing needs.
CNC routers are also an essential tool in both the music industry and fine arts. Their precision allows musicians and artists to create complex and detailed designs for a range of products, from musical instruments to sculptures.
Musical Instrument Manufacturing: The CNC router plays a critical role in the production of musical instruments, particularly those made from wood. Guitars, violins, and other string instruments often require precise carvings for their bodies and necks. CNC routers can accurately reproduce the required shapes, ensuring the final product delivers both visual beauty and sound quality. The accuracy provided by CNC routers also helps maintain consistent quality across all instruments produced.
Artistic Creations: Artists use CNC routers to bring their detailed designs to life, whether it’s creating sculptures, wall art, or intricate woodworks. The router’s ability to carve with precision allows for the creation of pieces that were once considered too complex or time-consuming to make by hand. This has opened up new possibilities for creative expression, especially in the realm of modern art.
In industries like aerospace and automotive manufacturing, where precision is critical for both safety and performance, CNC routers are invaluable tools for creating highly specialized components.
Custom Aerospace Parts: The aerospace industry relies on CNC routers to create custom parts for aircraft, spacecraft, and other related machinery. These parts must meet stringent requirements for strength and precision, and CNC routers are capable of achieving the level of detail needed for such critical components. Whether it's cutting structural elements or intricate design features, CNC routers help manufacturers meet the exact specifications required for high-performance aerospace products.
Vehicle Components: The automotive industry also benefits from the use of CNC routers. Car manufacturers use CNC routers to produce custom interior parts, dashboard components, and intricate body panels. The ability to work with both metal and composite materials allows automotive manufacturers to create lightweight yet durable parts that can withstand the stresses of daily driving.
Packaging is another significant industry where CNC routers are commonly used. The ability to cut foam into custom shapes allows for better protection of products during shipping and handling.
Foam Cutting: CNC routers can cut foam materials to fit custom packaging needs, offering a secure and protective solution for fragile products. The ability to create intricate, custom molds ensures that items are perfectly cushioned, reducing damage during transport.
Industrial Packaging: CNC routers are used to create specialized packaging inserts, such as foam molds for electronic devices or medical equipment. This level of customization is impossible with traditional manual methods, making CNC routers a valuable tool for manufacturers looking to improve packaging efficiency and safety.
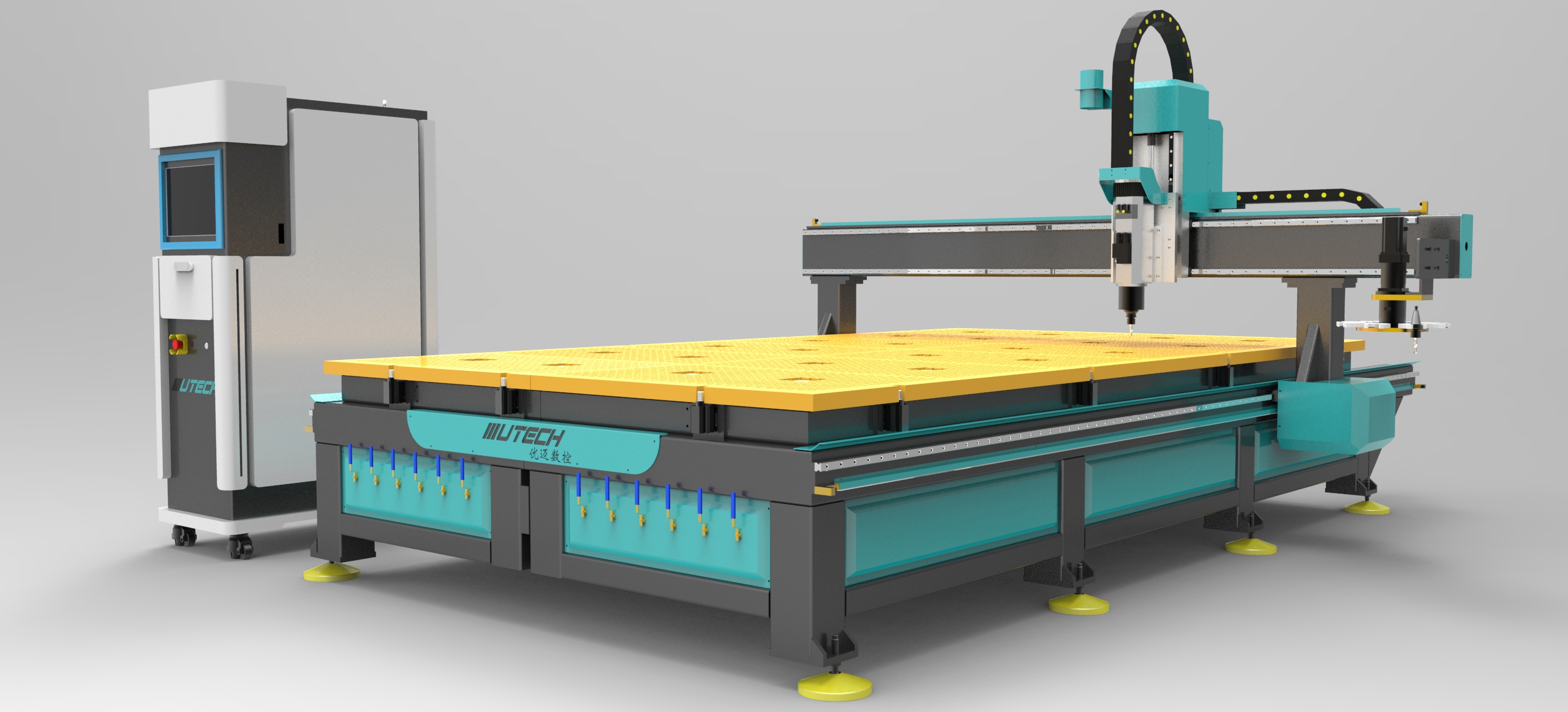
One of the main reasons industries use CNC routers is for their ability to produce precise and repeatable results. CNC routers ensure that the same part can be made thousands of times with exact specifications.
Accuracy: Whether cutting wood, plastic, or metal, CNC routers are known for their ability to achieve high levels of accuracy, making them the preferred choice for industries that require exact parts.
Consistency: CNC routers can reproduce the same design consistently, making them ideal for mass production. This consistency ensures that every part meets the required standards.
CNC routers are versatile machines capable of handling a wide range of materials, making them suitable for various industries. Whether you need to cut wood, metals, or foams, CNC routers can adapt to the requirements of the task.
Material Range: CNC routers are used to cut and engrave wood, plastic, foam, composites, and metals. This versatility makes them invaluable for businesses working in different sectors, from furniture manufacturing to aerospace.
Adaptability: The versatility of CNC routers means that businesses can easily switch between different materials, expanding their product offerings and capabilities.
CNC routers operate faster than traditional methods, improving productivity and reducing production time.
Production Rate: CNC routers can work continuously without requiring breaks, unlike human workers. This increases the production capacity, which is essential in high-demand industries.
Continuous Operation: The automation of the process allows CNC routers to operate for long periods, meeting deadlines and increasing overall production speed.
With CNC routers, there is less need for direct human involvement in the cutting process, reducing the risk of accidents.
Reduced Human Interaction: Since the CNC router is operated by a computer, the risk of injury from sharp tools is minimized. Operators can focus on overseeing the process rather than handling the cutting tools directly.
Reduced Risk of Injury: Automated operations ensure that the cutting process is efficient, reducing the likelihood of operator error and accidents in the workplace.
CNC routers come in a variety of configurations, each designed to meet the specific needs of different industries.
3-Axis vs 5-Axis Routers: A 3-axis CNC router moves along the X, Y, and Z axes, while a 5-axis router adds rotational movement, allowing for more complex cuts and shapes.
Desktop and Industrial Models: Smaller, desktop models are great for home-based projects or small businesses, while industrial models are built for high-volume production and can handle more demanding tasks.
CNC routers rely heavily on software to create and implement designs.
CAD/CAM Integration: CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software is used to create a design, which is then converted into machine-readable code by CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software.
G-code Programming: G-code is the language used by CNC routers to execute the cutting process, directing the router where and how to cut along specific coordinates.
The performance of a CNC router depends on its drive system and motors.
Drive Types: CNC routers use different drive systems, such as rack and pinion, lead screw, and ball screw, to move the router along its axes.
Motor Choices: Stepper motors and servo motors are the two main options, with stepper motors being less expensive and servo motors offering higher precision for high-speed applications.
While CNC routers excel at cutting soft materials, they do face challenges when cutting harder substances.
Handling Harder Materials: Materials like metal or stone require specialized bits and more advanced routers to handle them effectively.
Tool Wear and Maintenance: Different materials can wear out tools more quickly, requiring regular maintenance to keep the router in optimal condition.
CNC routers are a significant investment, but they offer long-term savings through increased productivity.
Initial Costs: The initial price of a CNC router can range from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars, depending on the size and functionality of the machine.
Long-Term Savings: Investing in a CNC router can save businesses money by reducing labor costs and improving production efficiency.
Operating a CNC router requires specialized skills and training.
Operator Skills: Operators must understand CAD/CAM software, G-code programming, and machine operation to fully utilize a CNC router.
Training Programs: Many CNC router manufacturers and businesses offer training programs to help operators gain the necessary skills.
CNC routers are versatile, efficient, and precise machines used across multiple industries, including woodworking and aerospace. They automate complex tasks, create intricate designs, and ensure repeatability, boosting productivity and precision. As industries adopt automation, CNC routers' future looks promising with emerging technologies. Companies like UTECH provide CNC routers that deliver exceptional value, enhancing production workflows and meeting evolving demands.
A: A CNC router is used for automating tasks like cutting, engraving, and shaping materials such as wood, plastic, and metals with precision.
A: A CNC router works by following computer-generated instructions, converting design files into G-code that directs the machine's movement along multiple axes.
A: CNC routers offer speed, precision, and repeatability, making them ideal for mass production, prototyping, and custom work across various industries.
A: CNC routers can handle a variety of materials, including wood, plastics, foam, and metals, making them versatile for different applications.
A: CNC router prices vary from a few thousand dollars for desktop models to tens of thousands for industrial models, depending on size and features.

























